Artisanal and Small-Scale mining (ASM) could be a powerful force for development
ASM supplies 20% of the global diamond trade and 20% of global output
A more socially and environmentally aware approach to ASM could affect 13 million people involved in ASM
Approximatly 100 million people in developing nations depend on ASM
ASM is more lucrative to local household income by a ratio of 3:5
Due to poverty, miners are driven by desperation, driving underpaid workers to ASM
ASM is a dangerous line of work and prone to exploitation of the nation's people
The current ASM practice causes harm to the environment that stimulates poverty and insecurity
Sierra Leone accoiunts fgor almost 38% of diamond exports, and includes as many as 120,000 people
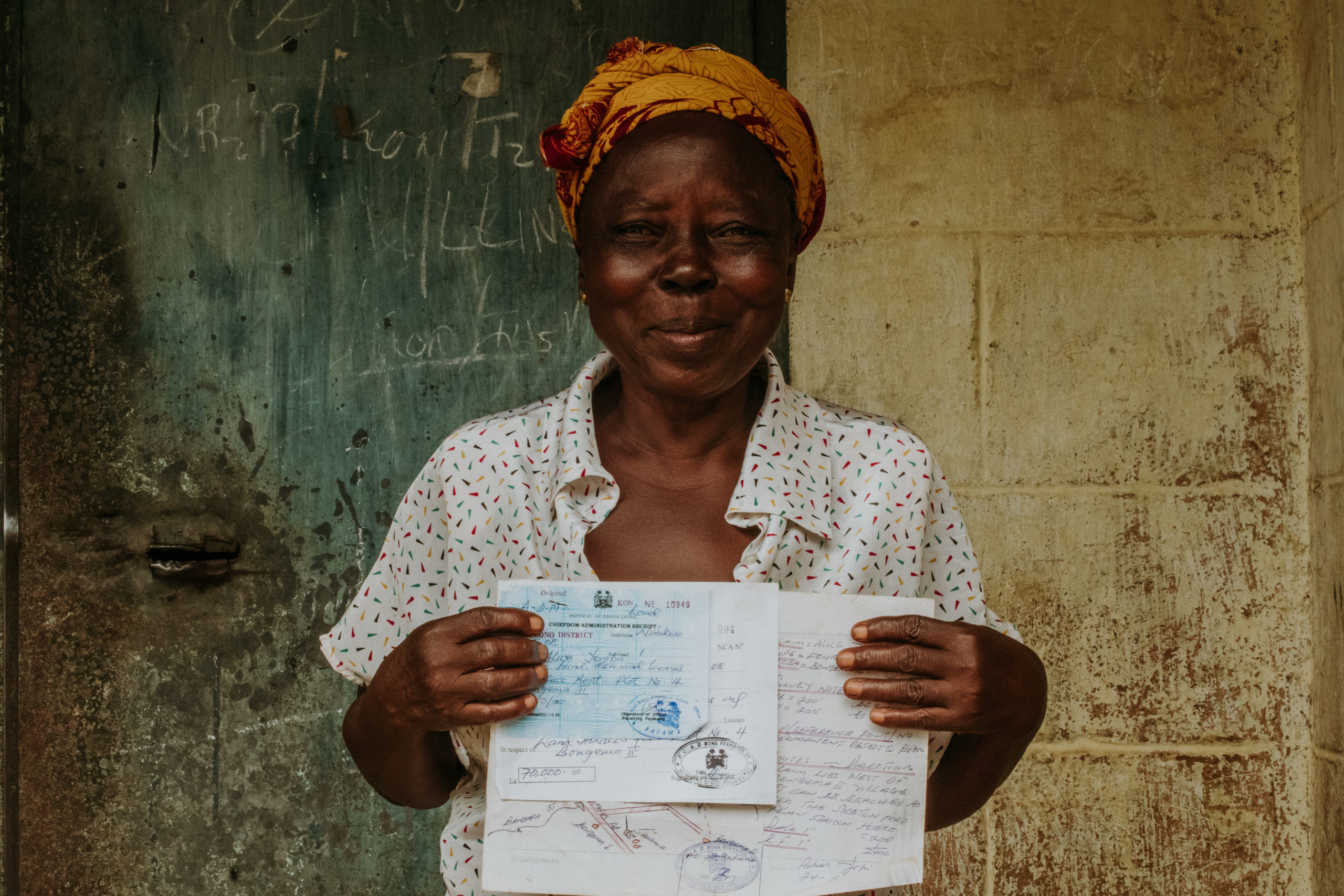
Mining communities are failing to profit from their own natural resource wealth
Sierra Leone currently ranks 183 out of 187 countries on the United Nation's Human Development Index (2014)
Export commodities are Iron ore, diamonds, rutile, cocoa, while imort commodities are foodstuffs, machinary and equipment , fuels and lubricants and chemicals
Negative ASM practices cause deforestation and biodiversity loss
The nation has 8 airports, with 1 runway of the 8 is paved.
The lack of land security, surface minerals and low physical barriers negatively affect ASM regulations
Smuggling minerals contributes to the the nation's insecurity and loss of federal tax revenue
Artisanl Diamond Miningdegrades the land, reducing farming opportunities
The current ASM practice systematicaly reduces economic opportunities for the nation's people
The ASM cycle of issues are not simple, direct, or inevitable
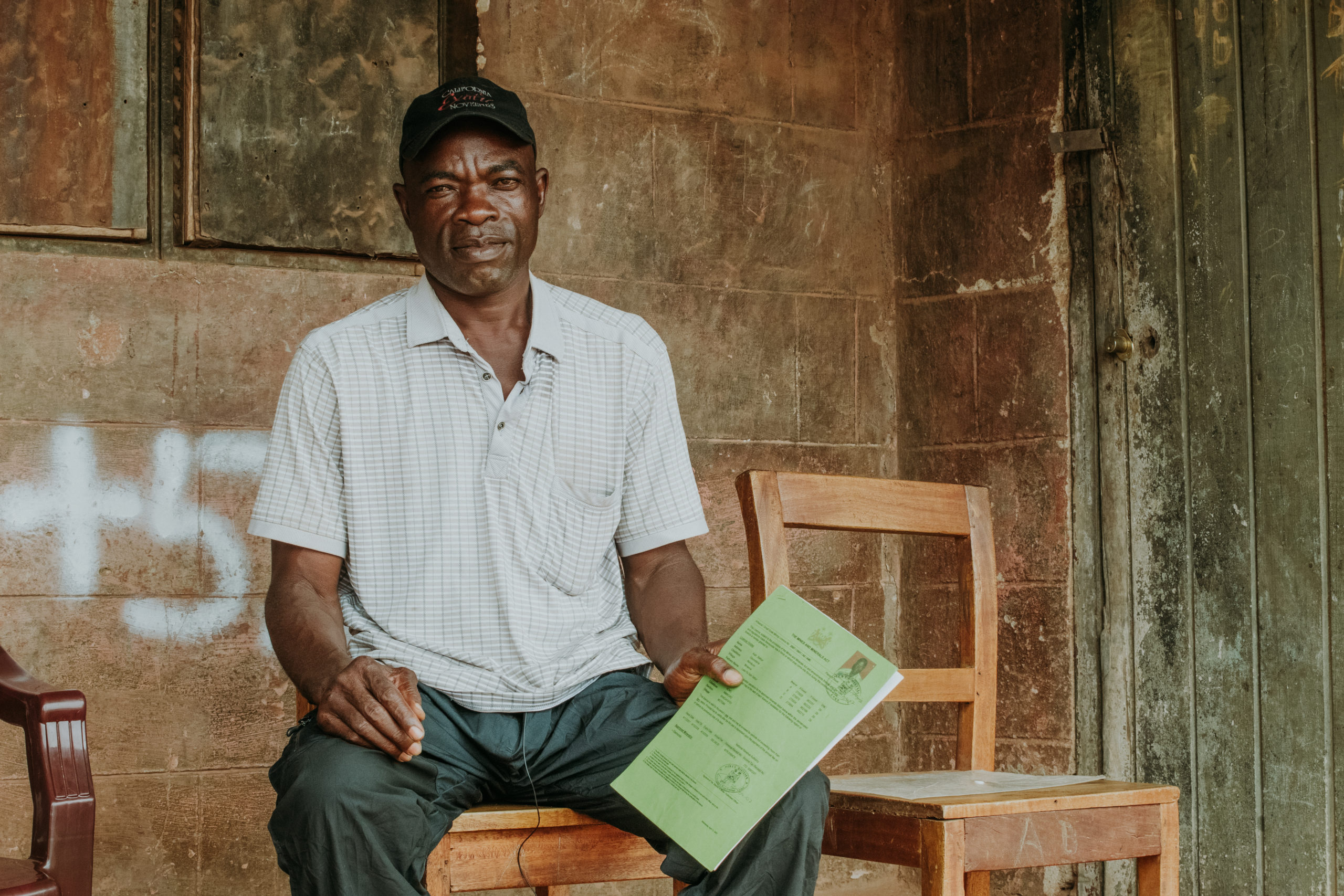
Miners and Landowners lack resources to pursue solutions
Mining communities lack institutional support
Geological factors create unqiue social challenges
Low barrier entry and distrubuted mineral deposits make regulation practices extremely difficult
Low standards for health, sanitation and saftey positions the current ASM culture as unethical
Low environmental management allows for the continuation of bad ASM practices
Damaged land generates a long chain of cause and effect
Polluted water systems caused by unmagaed ASM practices create fatal health problems
The open and abandoned mining pits collect water, breeding disease
Subsistence argricuture is almost half of the working population's form of survival
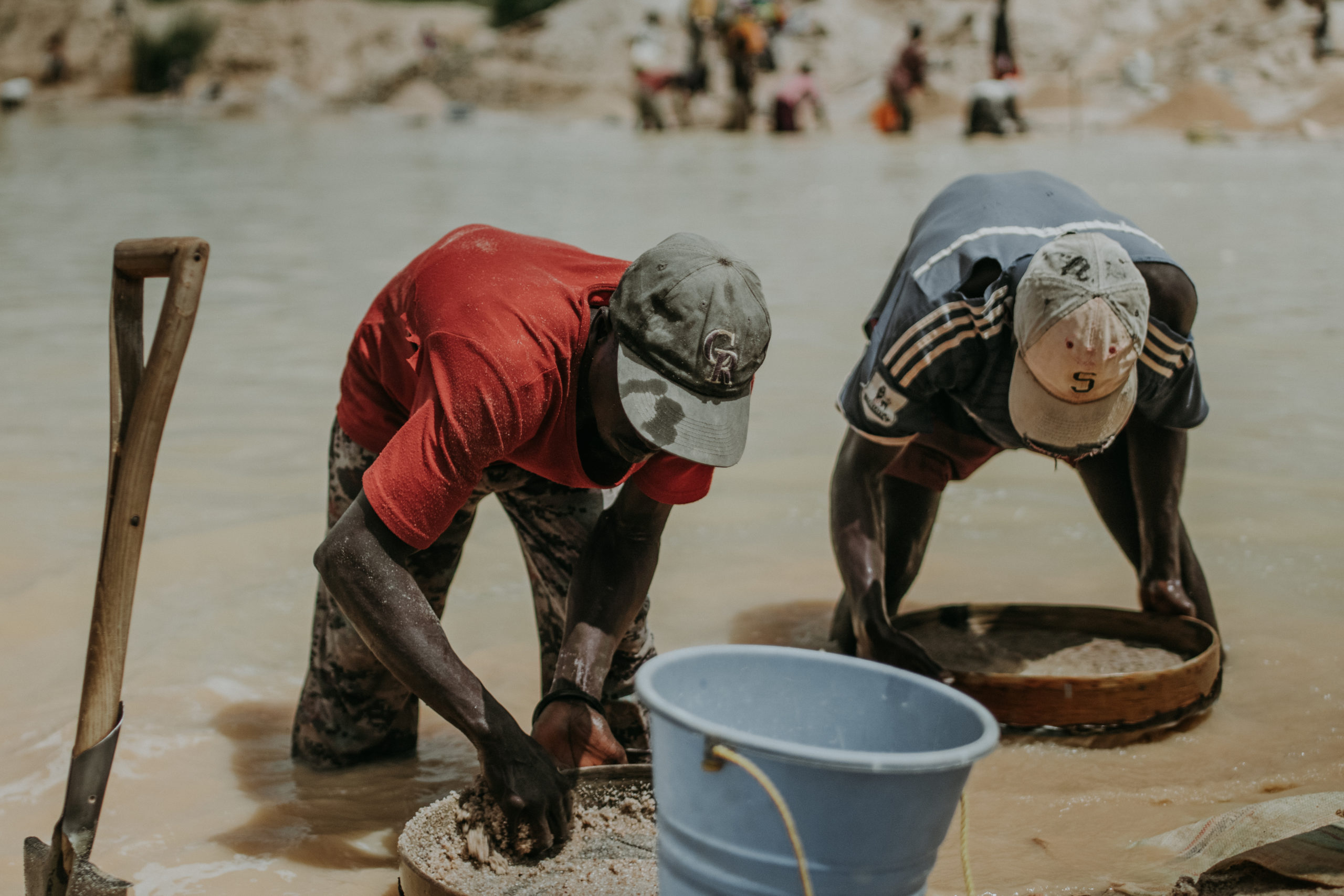
Labor-intesive operations are mostly performed by male adults and male youth
Seasonal mining is based on the raining seasons, causing unstable income
Miners have poor access to support, services and market knowledge
Inequitable profit sharing suppresses economic opportunities with low education and high percentage of poverty
The lack of economic development is the root cause to nations conflicts and exploitation
In 2017 exports of goods and services were at 26.8%, while imports of goods and services wer at -55.3%
Agriculture laborforce is approximitly 60%, while Industry laborforce is approximtely 6%
There is a passive governmental oversight of ASM environmental issues
Majority of the natural resource management is facilitated by NGOs, creating an unhealthy dependancy
The civil war created long lasting social economic instability and have not been properlly addressed for decades.
The global chairty ideology has generated layers of faulty strategies on African nations poverty
Artisanal diamond mining produces approx. half the world’s diamonds
During the year of 2019, 65,000 carats were produced out of one of many diamond producing nations
Over 1.9 billion carats have been traded throughout Africa valuing at approximately $158 billion
It is very difficult to provide journalistic access to information and access to ASM troubling details
ASM miners make less than $2 per day working in dangerous conditions
ASM working conditions are poor and not up to proper standards
It is difficult to locate the true percentage of illegal diamond trade and smuggling
the United Nations is still currently pushing for a strionger Kimberely Process System
Governmental corruption causes much of the negative impact on regulations and security processes
Child labor is a high percentage threat for diamonnd mining communities due to poverty
There is very little enforcement of regulations
Many miners lack bargaining power due to the lack of licensing